by Paul Barker, Konsulko Group
Introduction
Rust is a modern programming language which emerged from Mozilla Research around 2010 and has been stable since 2015 (see the history section of the Wikipedia article). Rust is an excellent fit for embedded software development due to its focus on performance and safety without the overhead of garbage collection or a large language runtime. The zero-cost abstractions provided by Rust support developer productivity, allowing the use of traits, generics, functional programming styles and other high-level approaches in the knowledge that the resulting assembly code will perform just as well as more verbose, hand written lower level code.
Now is a great time to pick up Rust if you work in the Embedded space. The Rust Embedded Working Group has produced an Embedded Rust Book for an audience with existing embedded development knowledge and the Discovery Book for an audience with no embedded experience but a desire to learn. The Linux kernel community has began discussing the use of Rust within the kernel itself and the OpenEmbedded/Yocto Project community is planning to move Rust support into the openembedded-core layer during the next release cycle.
The benefits of Rust largely stem from the language’s memory model, the borrow checker and other features which will be new to most developers learning Rust. The above resources from the Rust Embedded WG along with several published books and online tutorials cover this material well and so it will not be repeated in detail here. However, if you wish to develop software in Rust for production deployment you should expect to invest at least a few weeks in learning the language, assuming existing familiarity with other programming languages like C, Python or Java.
This article will introduce a couple of simple example applications written in Rust, discuss how to compile and run these applications natively on a Linux system using the Cargo build system and show how to create Yocto Project recipes for these applications using the cargo-bitbake tool. Some basic knowledge of the Yocto Project is assumed but no previous experience of Rust should be required.
Getting Started with Rust
In this section we will install Rust on our Linux system and create two simple applications.
Note that it is not necessary to have Rust installed natively in order to build applications and libraries written in Rust under bitbake. However, installing Rust natively does allow us to develop, test and debug applications on the host before we try to cross-compile them and it is an important step to take when learning Rust.
Installing Rust
The recommended way of installing Rust on a Linux system is to download and run the official installation script. When prompted with the installation options it is usually sufficient to select option 1 to use the defaults. This will install Rust in the current user’s home directory and modify the profile files to set necessary environment variables at login.
$ curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
<output snipped>
Current installation options:
default host triple: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
default toolchain: stable (default)
profile: default
modify PATH variable: yes
1) Proceed with installation (default)
2) Customize installation
3) Cancel installation
>1
<output snipped>
Rust is installed now. Great!
To get started you need Cargo's bin directory ($HOME/.cargo/bin) in your PATH
environment variable. Next time you log in this will be done
automatically.
To configure your current shell run source $HOME/.cargo/env
After installing Rust you should log out and log back in to ensure that environment variables are set correctly.
Hello, World
As is traditional, we will begin by looking at a “Hello, World” application.
Each Rust application or library should have its own project directory. Within this directory, the source code is usually placed in a src directory and the top level directory contains the Cargo config file for the project
and any other collateral files such as a README file, LICENSE file, etc.
To create our project directory and populate it with initial files we can use the cargo init command:
$ cargo init hello-rs
Created binary (application) package
Within our new hello-rs directory, this command creates an initial source file in src/main.rs with the following contents:
fn main() {
println!("Hello, world!");
}
This makes our job of writing a Hello World application very simple – no code modifications are needed!
The cargo init command also creates a Cargo.toml file in our project directory to store project configuration and metadata:
[package]
name = "hello-rs"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Paul Barker <pbarker@konsulko.com>"]
edition = "2018"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[dependencies]
We should test our new Hello World application natively before we try to cross-compile it under bitbake. To do this we can use the cargo build and cargo run commands:
$ cargo build
Compiling hello v0.1.0 (/home/pbarker/Projects/Rust/rust/hello-rs)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.29s
$ cargo run
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.01s
Running `target/debug/hello-rs`
Hello, world!
The last stage for our hello world application is to publish it as a git repository so that it can be fetched and built in our Yocto Project environment. We should create a LICENSE file and a README file in the top level of the project for the benefit of anyone who wants to reuse our code. My preference is for the Apache license version 2.0 but feel free to use any appropriate open source license here.
We should also add some extra metadata to the Cargo.toml file to specify the license, briefly describe the project and link to the location where we will be publishing the repository. This metadata will be used by cargo-bitbake when we generate a recipe for our application. In my case the repository will be published to my GitLab account.
--- a/Cargo.toml
+++ b/Cargo.toml
@@ -3,6 +3,9 @@ name = "hello-rs"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Paul Barker <pbarker@konsulko.com>"]
edition = "2018"
+license = "Apache-2.0"
+description = "Hello World application"
+repository = "https://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/hello-rs.git"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
To finish up, commit the project files to a git repository and push to a location which can be reached when building using Yocto Project. Alternatively, you can make use of the hello-rs repository I published under my GitLab account.
print-rand
The Hello World application above will demonstrate only part of the capabilities of the cargo-bitbake tool and the Rust support in Yocto Project. To see how Rust dependencies are handled in Yocto Project we’ll need an application which actually depends on a Rust library (known as a crate). The print-rand application will fill this role as it uses the rand crate to generate random numbers.
As before we will start by creating the project using cargo init:
$ cargo init print-rand
Created binary (application) package
We will now modify the src/main.rs file to generate and print a random number:
use rand::prelude::*;
fn main() {
let x: u32 = random();
println!("x = {}", x);
}
We will also modify the Cargo.toml file to list the rand crate as a dependency:
[package]
name = "print-rand"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Paul Barker <pbarker@konsulko.com>"]
edition = "2018"
[dependencies]
rand = "0.7"
We can build and test this application in a similar way to the previous Hello World app. Note that each dependency is downloaded and built along the way:
$ cargo build
Compiling libc v0.2.77
Compiling getrandom v0.1.15
Compiling cfg-if v0.1.10
Compiling ppv-lite86 v0.2.9
Compiling rand_core v0.5.1
Compiling rand_chacha v0.2.2
Compiling rand v0.7.3
Compiling print-rand v0.1.0 (/home/pbarker/Projects/Rust/rust/print-rand)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 3.60s
$ cargo run
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.01s
Running `target/debug/print-rand`
x = 643356417
As before, we should add LICENSE and README files at this stage and extend the metadata in the Cargo.toml file:
--- a/Cargo.toml
+++ b/Cargo.toml
@@ -3,6 +3,9 @@ name = "print-rand"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Paul Barker <pbarker@konsulko.com>"]
edition = "2018"
+license = "Apache-2.0"
+description = "Print a random number"
+repository = "https://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/print-rand.git"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
Lastly, commit the project files to a git repository and push to a public location. As before you may alternatively make use of the print-rand repository I published under my GitLab account.
Using cargo-bitbake
Now that we have created a couple of simple Rust applications and published them we can look at creating bitbake recipes using the cargo-bitbake tool. The first step of this process is to install the tool itself:
$ cargo install cargo-bitbake
<output snipped>
Compiling cargo-bitbake v0.3.14
Finished release [optimized] target(s) in 12m 30s
Installing /home/debian/.cargo/bin/cargo-bitbake
Installed package `cargo-bitbake v0.3.14` (executable `cargo-bitbake`)
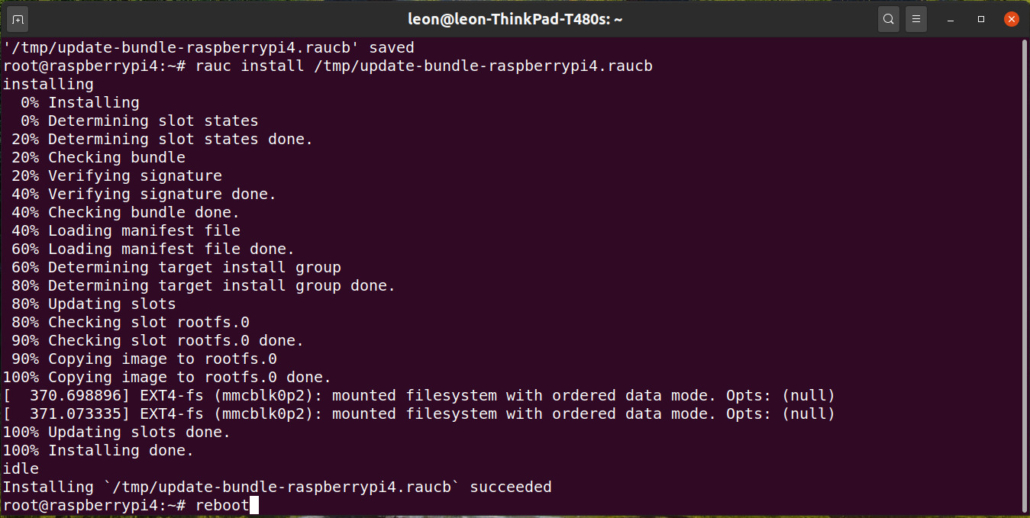
Before we run cargo bitbake for each our projects we should ensure that all changes are committed and pushed to the remote repository. We should also check the remote URL for each repository as this will be used to set SRC_URI. If the remote URL uses SSH access then you should ensure that this can be reached using an SSH key from the Yocto build environment or switch to HTTPS access.
Once we’re happy with the state of our repository we can run cargo bitbake in the top directory of our hello-rs project (note that we use a space not a dash in the command here):
$ cargo bitbake
No package.homepage set in your Cargo.toml, trying package.repository
Wrote: hello_0.1.0.bb
The message printed by cargo bitbake indicates that the repository entry in our Cargo.toml file was used as the homepage URL since we did not specify a separate homepage.
We can now look at the generated recipe file hello-rs_0.1.0.bb:
# Auto-Generated by cargo-bitbake 0.3.14
#
inherit cargo
# If this is git based prefer versioned ones if they exist
# DEFAULT_PREFERENCE = "-1"
# how to get hello-rs could be as easy as but default to a git checkout:
# SRC_URI += "crate://crates.io/hello-rs/0.1.0"
SRC_URI += "git://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/hello-rs.git;protocol=https;nobranch=1;branch=dev"
SRCREV = "cec42fb0d147e4a4b271256c475620ff627c8856"
S = "${WORKDIR}/git"
CARGO_SRC_DIR = ""
# please note if you have entries that do not begin with crate://
# you must change them to how that package can be fetched
SRC_URI += " \
"
# FIXME: update generateme with the real MD5 of the license file
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = " \
file://LICENSE;md5=86d3f3a95c324c9479bd8986968f4327 \
"
SUMMARY = "Hello World application"
HOMEPAGE = "https://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/hello-rs.git"
LICENSE = "Apache-2.0"
# includes this file if it exists but does not fail
# this is useful for anything you may want to override from
# what cargo-bitbake generates.
include hello-rs-${PV}.inc
include hello-rs.inc
As we noted above, the SRC_URI and SRCREV entries are based on the remote URI and the currently checked out commit of our local git repository. The SUMMARY, HOMEPAGE and LICENSE entries are based on the metadata in our Cargo.toml file. The LIC_FILES_CHKSUM entry is set based on the LICENSE file in our project.
We can also generate a recipe for the print-rand project by running cargo bitbake in the top directory of this project:
$ cargo bitbake
No package.homepage set in your Cargo.toml, trying package.repository
Wrote: print-rand_0.1.0.bb
The print-rand_0.1.0.bb recipe is very similar to the previous recipe for our hello world application. The SRC_URI, SRCREV, SUMMARY and HOMEPAGE are changed to the appropriate values for this project. The SRC_URI variable is extended with a list of the dependency crates required by this project, this includes not just the rand crate that we explicitly listed as a dependency in our Cargo.toml file but also all the recursive dependencies of this crate.
# Auto-Generated by cargo-bitbake 0.3.14
#
inherit cargo
# If this is git based prefer versioned ones if they exist
# DEFAULT_PREFERENCE = "-1"
# how to get print-rand could be as easy as but default to a git checkout:
# SRC_URI += "crate://crates.io/print-rand/0.1.0"
SRC_URI += "git://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/print-rand.git;protocol=https;nobranch=1;branch=dev"
SRCREV = "3397247f929f28d70adbb65d3990dc72699553bb"
S = "${WORKDIR}/git"
CARGO_SRC_DIR = ""
# please note if you have entries that do not begin with crate://
# you must change them to how that package can be fetched
SRC_URI += " \
crate://crates.io/cfg-if/0.1.10 \
crate://crates.io/getrandom/0.1.15 \
crate://crates.io/libc/0.2.79 \
crate://crates.io/ppv-lite86/0.2.9 \
crate://crates.io/rand/0.7.3 \
crate://crates.io/rand_chacha/0.2.2 \
crate://crates.io/rand_core/0.5.1 \
crate://crates.io/rand_hc/0.2.0 \
crate://crates.io/wasi/0.9.0+wasi-snapshot-preview1 \
"
# FIXME: update generateme with the real MD5 of the license file
LIC_FILES_CHKSUM = " \
file://LICENSE;md5=86d3f3a95c324c9479bd8986968f4327 \
"
SUMMARY = "Print a random number"
HOMEPAGE = "https://gitlab.com/pbarker.dev/rust/print-rand.git"
LICENSE = "Apache-2.0"
# includes this file if it exists but does not fail
# this is useful for anything you may want to override from
# what cargo-bitbake generates.
include print-rand-${PV}.inc
include print-rand.inc
We can now add these recipes to a Yocto Project layer and build them using bitbake. Support for the Rust toolchain in Yocto Project is provided by the meta-rust layer so this layer must be included before these recipes can be built. As there are many ways to put together a Yocto Project build we won’t cover this in this blog post. However, you can see a walkthrough of this process in the Using Rust with Yocto Project demo presented at theYocto Project Summit Europe 2020.